Researchers from Japan established a novel system to understand how individual muscles coordinate with each other during physical activity
Surface electromyography (sEMG) is a non-invasive method that measures the electrical activity of muscles to assess activity and fatigue. Current approaches do not evaluate multiple muscles at the same time, which is important for understanding how individual muscles coordinate with each other during physical activity. In this study, researchers from Japan established a novel measurement system to assess forearm fatigue and create visually informative maps during a grasping task.
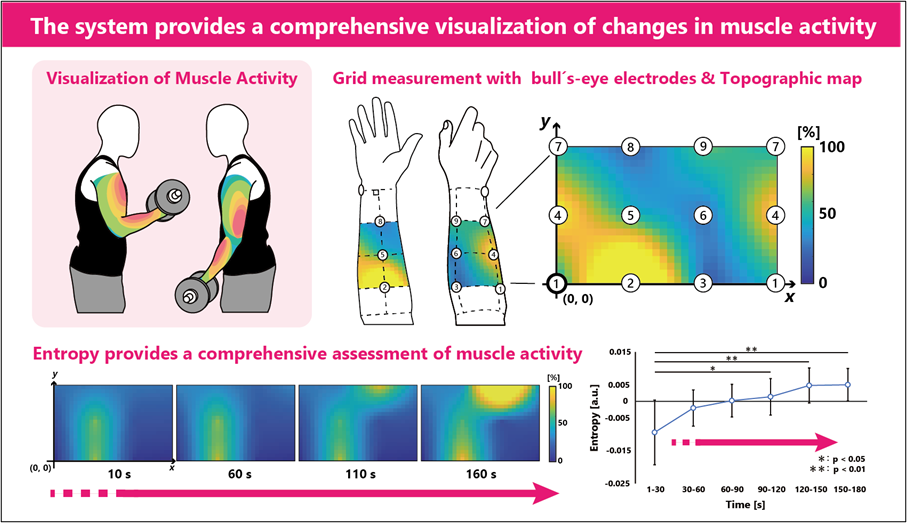
Image title: Researchers use bull’s-eye electrodes to better understand muscle coordination regardless of the direction of muscle fibers
Image caption: The traditional sEMG approaches are unable to evaluate the activity of multiple muscles at the same time. This is important to study the coordination of muscles in the human body. To overcome this limitation, researchers from Japan have established a novel measurement system and demonstrated its effectiveness.
Image credit: Ms. Megumi Shimura and Dr. Yoshihiro Shimomura, Chiba University, Japan
Image license: Original content
Usage restrictions: Cannot be reused without permission
Surface electromyography (sEMG) is a traditional method used to measure the electrical activity of muscles during physical activity. This method has remained unchanged for over 70 years and involves the use of two standard approaches. The first involves a pair of electrodes—metals that conduct electricity through non-metals—to record from a particular muscle, while the second employs a grid of electrodes arranged in a small rectangular layout in order to measure the potential distribution of intra-muscle activity. However, these approaches only provide a measurement of a single muscle at a time. Thus, limiting our understanding of how our muscles coordinate while carrying out various physical activities.
In a new study published in the Journal of Physiological Anthropology on 27 October 2023, Professor Yoshihiro Shimomura of the Design Research Institute, Chiba University, along with a team of researchers, demonstrated the use of bull’s-eye electrodes to evaluate the activity of multiple muscles at the same time and investigated its ability to assess fatigue and develop visuals of muscle coordination during a grasping task. His team included Ms. Megumi Shimura and Mr. Akihiko Mizumoto from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering, and Dr. Yali Xia from Design Research Institute, Chiba University.
“Ours is the first study to provide images of muscle coordination in the human body and to revolutionize the existing methodology of electromyography,” explains Dr. Shimomura.
The researchers enrolled nine adults without any injuries or health issues for this study. The participants were asked to perform a grasping task. In this task, a pulley system with a handle at one end and a weight at the other end was employed, and the participants were instructed to grasp the handle with the hand most frequently used without moving the forearm. During the task, the bull’s-eye electrode measured the activity of muscles. The performance of this system was assessed using root mean square and entropy—a measure of the disorder of a system.
The findings suggest that an increase in entropy over time indicates an increase in the disorder of forearm muscle due to fatigue. In addition, bull’s-eye electrodes provided an image of muscle activity at nine different points. Thus, the study forms a base for further development of a multichannel sEMG system to increase the scope of measuring muscle activity. “Although our bull’s-eye electrode system has some limitations such as electric gain, it is a robust system that illustrates the muscle activity due to fatigue,” elaborates Dr. Shimomura
Dr. Shimomura concludes, “Having access to an electromyogram can aid in the treatment of muscle disorders of people working in urban lifestyles and improve the health of elderly people. It can also successfully transform the use of one’s body to improve the health and quality of life. Going forward, being able to better understand our electromyogram is likely to change the way we use our bodies and enhance our well-being.”
About Professor Yoshihiro Shimomura
Dr. Yoshihiro Shimomura is a professor at the Design Research Institute, Chiba University, and his research interests include design, ergonomics, and physiological anthropology. He earned his Ph.D. in Engineering from Chiba University in Japan. Dr. Shimomura has published more than 100 research articles and has been felicitated with 25 prestigious awards. He has also been elected to several prominent committees, received grants from more than 100 collaboration works with companies, and maintains 13 patents.
Funding:
This study was supported by the JST SPRING (grant number: JPMJSP2109)
Reference:
Title of original paper: Multipoint surface electromyography measurement using bull’s‑eye electrodes for wide‑area topographic analysis
Authors: Megumi Shimura1*, Akihiko Mizumoto1, Yali Xia2 and Yoshihiro Shimomura2
Affiliations: 1Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Chiba University
2Design Research Institute, Chiba University
Journal: Journal of Physiological Anthropology
DOI: 10.1186/s40101-023-00342-3
Contact: Megumi Shimura
Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Chiba University
Email: m-shimura@chiba-u.jp
Public Relations Office, Chiba University
Address: 1-33 Yayoi, Inage, Chiba 263-8522 JAPAN
Email: koho-press@chiba-u.jp
Tel: +81-43-290-2018
Recommend
-

The role of the Research Institute of Disaster Medicine (RIDM): The indispensable research hub for urban digital transformation
2023.02.23
-

CUTICULA: A Secret of Unique Body Shape of Insects −Exploring the Sophisticated Mechanism Behind their Elongated and Round Bodies
2023.12.11
-

Unlocking the Enigma of Dark Matter: Gazing Beyond the Lens into the Universe
2023.06.09


